Managing Cardiac Arrest and Medications used in Cardiac arrest
Cardiac arrest (CA) can be defined as the acute loss of heart function, either instantaneously or following a range of symptoms, ultimately leading to an arrest of circulation.
Clinically, the three classic characterizing features of Cardiac arrest are :
- Pulselessness
- Unresponsiveness and
- Abnormal breathing — either agonal or absent.
The estimated annual incidence of out-of-hospital Cardiac arrest ranges anywhere from 250,000 to 420,000 and is still one of most common causes of death in the United States. There is a multitude of underlying etiologies with ischemic heart disease being the most common.
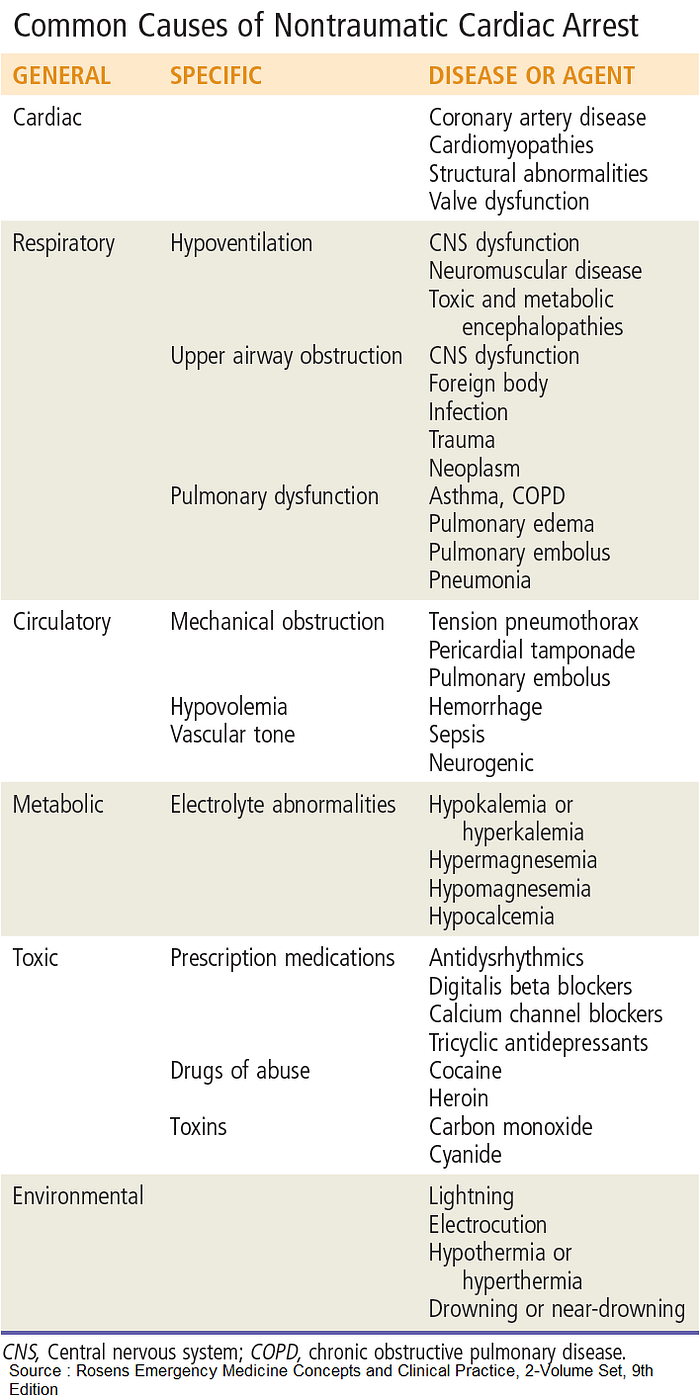
There are four main conduction rhythms of Cardiac arrest :
Shockable with a more favorable outcome:
- Ventricular fibrillation (VF)
- Pulseless ventricular tachycardia (pVT).
Nonshockable:
- Pulseless electrical activity (PEA)
- Asystole.

Read Full Article Here : https://manualofmedicine.com/topics/emergency-acute-medicine/managing-cardiac-arrest/
